PLASMA InPlaceTransformation module PLASMA is a software package provided by Univ. of Tennessee, Univ. of California Berkeley and Univ. of Colorado Denver
This work is the implementation of an inplace transformation based on the GKK algorithm by Gustavson, Karlsson, Kagstrom and its fortran implementation.
- Version:
- 2.4.5
- Author:
- Mathieu Faverge
- Date:
- 2010-11-15
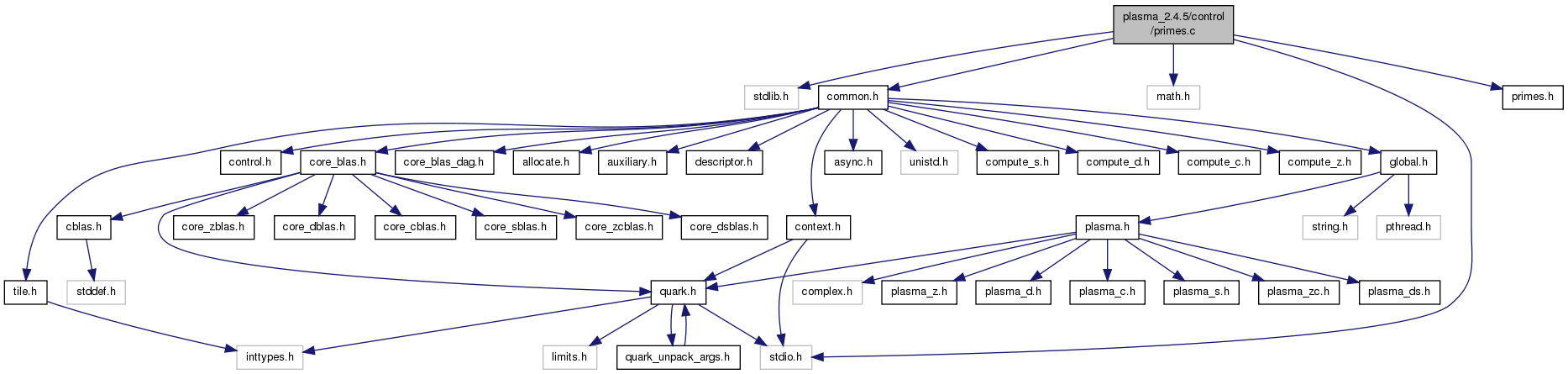
Definition in file primes.c.
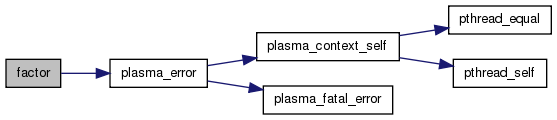
factor Factors an integer into a product of prime powers.
- Parameters:
-
| [in] | n | |
| [out] | pr | Array of size PRIME_MAXSIZE On exit, contains the prime factor of n modulo m |
| [out] | nf | Number of prime factor in n. |
Definition at line 748 of file primes.c.
References primedec::e, lapack_testing::f, primedec::p, primedec::pe, plasma_error(), PRIME_MAXSIZE, primes, and PRIMESTABLE_SIZE.
{
lnf = 0;
x = n;
sqrtx = (int)sqrt((double)x);
i = 0;
f = 1;
while( x > 1 ) {
if( f > sqrtx ) {
plasma_error(__func__,
"input matrix pr has too few columns");
}
lnf++;
break;
}
if( (x % f) == 0 ) {
plasma_error(__func__,
"input matrix pr has too few columns");
}
while( (x % f) == 0 ) {
}
sqrtx = (int)sqrt((double)x);
lnf++;
}
i++;
}
}
*nf = lnf;
}