|
QUARK
0.9.0
QUARK-QUeuingAndRuntimeforKernels
|
|
QUARK
0.9.0
QUARK-QUeuingAndRuntimeforKernels
|
#include <stdio.h>#include <stdlib.h>#include <assert.h>#include <math.h>#include <sys/time.h>#include <string.h>#include "quark.h"
Go to the source code of this file.
Functions/Subroutines | |
| void | matmul (double *A, double *B, double *C, int NB) |
| void | matmul_quark_task (Quark *quark) |
| void | matmul_quark_call (Quark *quark, double *A, double *B, double *C, int NB) |
| void | matrix_print (char *label, double *A, int N) |
| int | matrix_compare (double *A, double *A2, int N) |
| double | timeval_subtract (struct timeval *result, struct timeval *x, struct timeval *y) |
| void | std_to_bdl (double *A, double *Ablk, int N, int NB) |
| void | bdl_to_std (double *A, double *Ablk, int N, int NB) |
| int | main_algorithm (int NB, int N, int THREADS) |
| int | main (int argc, char **argv) |
| void bdl_to_std | ( | double * | A, |
| double * | Ablk, | ||
| int | N, | ||
| int | NB | ||
| ) |
Definition at line 135 of file matmul_example.c.
| int main | ( | int | argc, |
| char ** | argv | ||
| ) |
Definition at line 245 of file matmul_example.c.
References main_algorithm().
| int main_algorithm | ( | int | NB, |
| int | N, | ||
| int | THREADS | ||
| ) |
Definition at line 151 of file matmul_example.c.
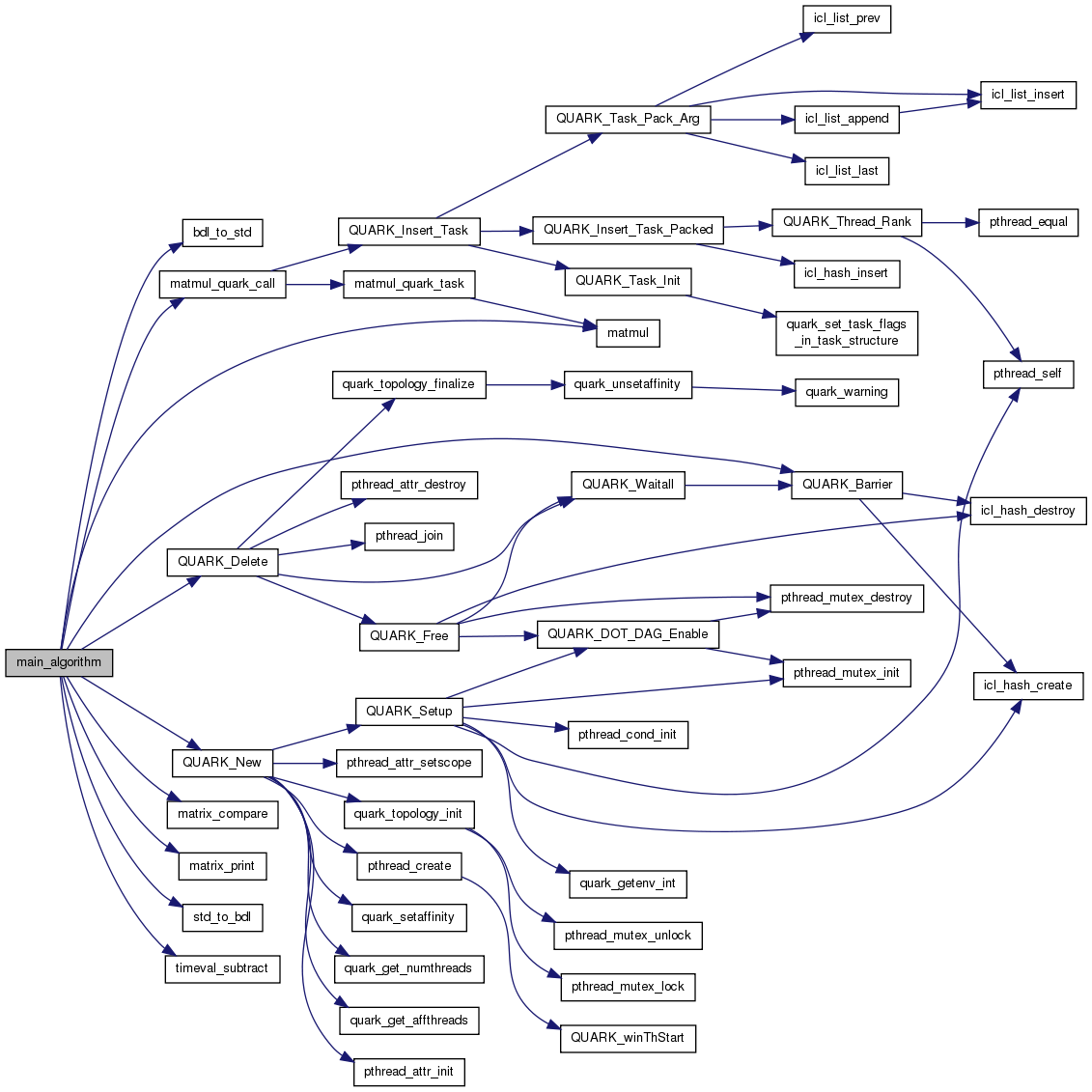
References bdl_to_std(), matmul(), matmul_quark_call(), matrix_compare(), matrix_print(), QUARK_Barrier(), QUARK_Delete(), QUARK_New(), std_to_bdl(), and timeval_subtract().
| void matmul | ( | double * | A, |
| double * | B, | ||
| double * | C, | ||
| int | NB | ||
| ) |
Definition at line 33 of file matmul_example.c.

| void matmul_quark_call | ( | Quark * | quark, |
| double * | A, | ||
| double * | B, | ||
| double * | C, | ||
| int | NB | ||
| ) |
Definition at line 60 of file matmul_example.c.
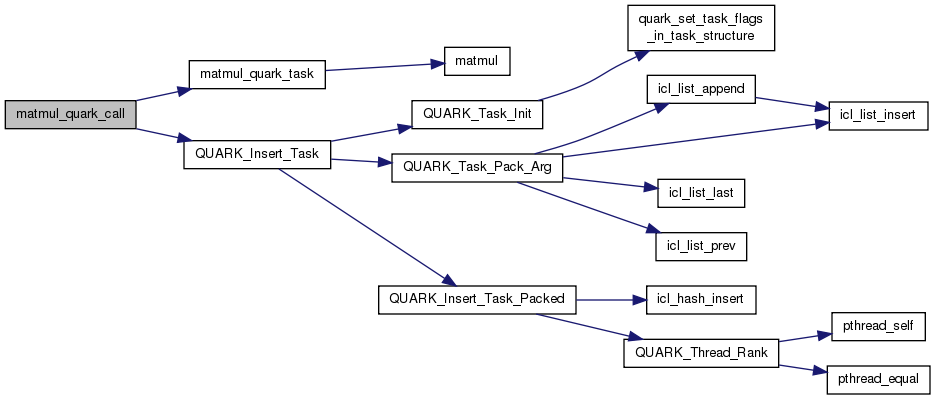
References INOUT, INPUT, matmul_quark_task(), QUARK_Insert_Task(), and VALUE.
| void matmul_quark_task | ( | Quark * | quark | ) |
Definition at line 47 of file matmul_example.c.
References matmul(), and quark_unpack_args_4.

| int matrix_compare | ( | double * | A, |
| double * | A2, | ||
| int | N | ||
| ) |
Definition at line 84 of file matmul_example.c.
| void matrix_print | ( | char * | label, |
| double * | A, | ||
| int | N | ||
| ) |
Definition at line 71 of file matmul_example.c.
| void std_to_bdl | ( | double * | A, |
| double * | Ablk, | ||
| int | N, | ||
| int | NB | ||
| ) |
Definition at line 123 of file matmul_example.c.
| double timeval_subtract | ( | struct timeval * | result, |
| struct timeval * | x, | ||
| struct timeval * | y | ||
| ) |
Definition at line 101 of file matmul_example.c.